通用学习设计
Universal design for learning (UDL) is an approach to designing course instruction, 材料, and content so that all students are able to access learning with a diminished need for retrofitting or accommodation. The concepts behind UDL encourage instructors to create flexibility and choice in their courses to the maximum extent possible so that unintended barriers to learning can be avoided or diminished.
观看高等教育中UDL的简短视频 特种应用技术澳门威尼斯人网上赌场中心 (CAST)的澳门威尼斯人网上赌场人员开发了UDL.
UDL原则
三个基于澳门威尼斯人网上赌场的 UDL原则 provide a framework for optimizing learning for all students.
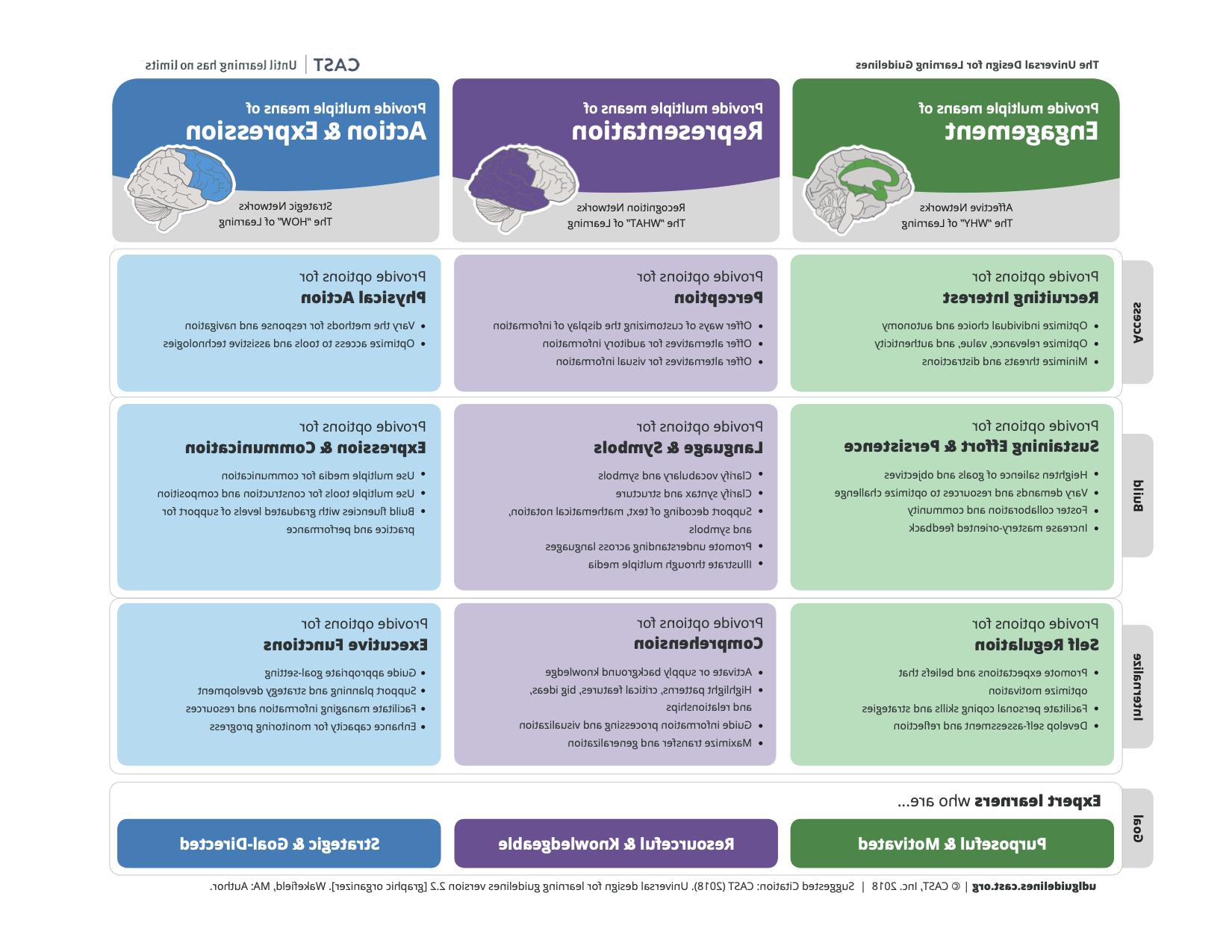
1. 多种参与方式
Provide options and a variety of ways for students to interact with the course content, 他们的同学, 和你, 作为导师. Allow students to make choices in as many aspects of the course as possible, 从而建立他们的自治和自决.
2. 多元代表方式
Present content in different formats and allow students to choose the formats in which they learn best. Provide text options when audio is used and audio or text options where visuals are used. This allows students to gain access to content via the methods most accessible to them.
3. 多种行动方式 & 表达式
Create different ways for students to demonstrate understanding. Certain types of assessments can create barriers for some learners. Providing choice helps them avoid those barriers and better demonstrate what they know. Also, offer different ways for students to communicate and participate during class.
通用设计学习指南
参观 把网站 for an accessible, interactive version of these guidelines.
UDL策略
在指令
- 使用一种以上的方法来呈现信息. 如果是传统的讲课形式, include slides or other visuals to support any auditory instruction. If using a visual diagram to demonstrate a concept, also include a written or audio description.
- 在每堂课开始前,将幻灯片邮寄或通过电子邮件发送. This allows students to focus the auditory content and discussion in class, rather than trying to copy down information from a slide.
- 改变课程的节奏. Keep lessons moving but allow time for individual and group interaction with the content.
- 分享笔记. Ask a student to share a copy of their notes with the class or consider having students crowdsource notes on a shared Google document. This is a great way to help students learn collaboratively and clear up misunderstandings in real time.
- 把你的课录下来,然后把视频上传到Blackboard上. This allows students to return to the lecture to clarify misunderstandings or missed content.
- 提供具体的例子和应用. Don’t assume that students are able to generalize the content – show them how it’s done. 将内容与现实联系起来, concrete examples helps to build understandings and transfer of skills.
在制定课程政策时
- 确定什么是必要的. Be purposeful when creating learning objectives and course standards. This will help you identify areas in which flexibility may be possible. Make sure these objectives are clearly stated for students.
- 明确期望. Provide students with detailed instructions and expectations for all components of your course, 包括作业, 参与, 和分级.
- 在截止日期上建立灵活性. 残疾状况的爆发, 生活事件, and access to resources can impact a student’s ability to complete their work. Building in a reasonable degree of flexibility with deadlines helps to prevent students from being penalized for circumstances outside of their control.
- Consider how attendance requirements align with course objectives. Are students able to complete the learning in the course without attending each class? 如果是的话,放松你的出勤标准. If much of the earning is completed in class and attendance is, 因此, 必要的, 一定要让你的学生明白这一点.
在设计评估时
- 提供频繁的、个性化的反馈. This allows students to better gauge their understandings of the content and better direct their learning.
- 取消定时评估. 时间限制会给很多学生造成障碍, including many students with disabilities and students for whom English is not their first language.
- 为评估提供选择. 允许学生选择(例如., paper or presentation; exam or project) for demonstrating their understandings helps to remove barriers that are created by certain types of assessments.
- 在考试中使用不同类型的问题. If exams are still your best option for assessment, vary the types of questions used. 学生 may run into barriers with certain formats (eg., 选择题或真/假), so providing a variety can help with demonstrating where students are actually struggling with the content vs. 纠结于问题的形式.
对UDL感到不知所措?
从+ 1策略开始. Choose one topic or area where your students seem to struggle. 要么
- Add ONE new way to present the content (add a video, a visual, a website, etc.)
OR - Add ONE new activity for students to complete (discussion, group project, quiz, etc.)
OR - Add ONE new way to assess understanding (paper, project, presentation, etc.)
When you’ve added this one new option to your course and feel comfortable with it, 选择另一个区域并使用+ 1策略. 创建一个普遍设计的课程需要时间. 这并不需要一夜之间完成.
关于UDL的其他参考资料
- 校园UDL:来自CAST (UDL框架的开发人员)的指南
- DO-IT的教育通用设计中心:来自华盛顿大学的资源